摘要
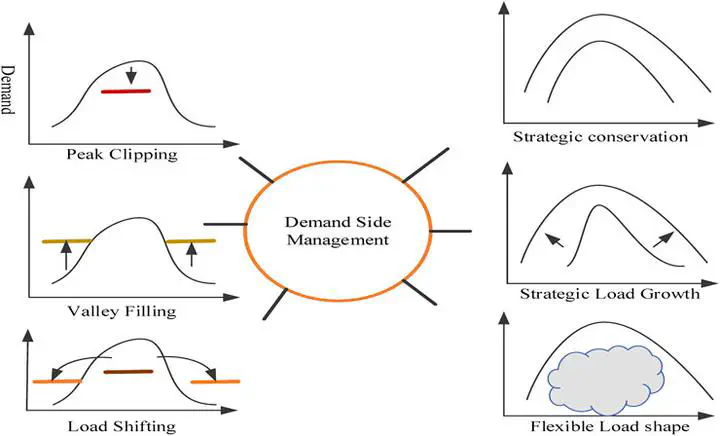
Self-sustaining microgrids (MG) are now possible due to the integration of renewable energy and communication technology in utility. It is essential to have an effective energy management system (EMS) because of the unpredictable response of these resources, the uncertainty of the load variations, and the market pricing. Only operational expenses have been considered while discussing MG’s optimum operation so far. It is necessary to examine the potential of adding demand-side management (DSM) to the energy management system challenges and its impact on overall operational costs and peak reduction. This article investigates the influence of the load shaping approach that is imposed by the utility on non-dispatchable energy sources. A stochastic EMS framework is developed to come up with an optimum solution for day-ahead scheduling and minimize operating costs for grid-connected MG. Using real-time weather data, four different solar and wind power production profiles are developed in the first step to address the issue of unpredictability. MG system design, operational restrictions, and allocating demand side management load participation data to the goal function are all addressed in this second step of the algorithm development. Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) is designed in the third stage to find the ideal setup of DG units for maximum electricity dispatch and comparing outcomes for all scenarios with and without DSM involvement. It has been shown that with a 20% DSM load participation, a proposed stochastic framework may save costs by 62%, according to the simulation results.