摘要
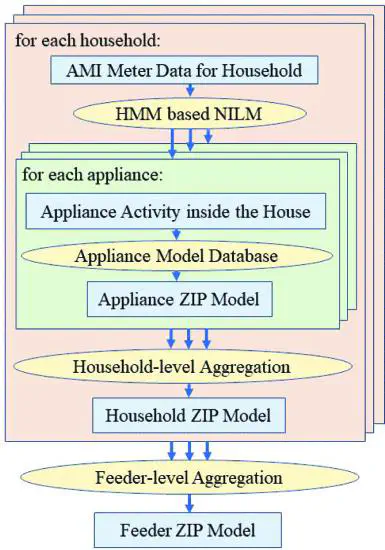
Aggregated load modeling is an important daily practice in utility companies, but existing statistics- or measurement-based methods suffer from various limitations. This work proposes an effective approach to identify ZIP coefficients of the aggregated residential load model using advanced measurement infrastructure (AMI) data. A non-intrusive load monitoring (NILM) based algorithm is developed to disaggregate household power consumption into appliance-level activities. Such appliance activities are then associated with ZIP attributes and aggregated to household and feeder level. Therefore, the equivalent ZIP coefficients are obtained without the dependence of other information. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is verified using a real-world smart meter data set and the IEEE 34-bus feeder test case.